Fejemis Teensy
(→Setup - loop overview) |
(→Setup - loop overview) |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
state.setup(); | state.setup(); | ||
} | } | ||
| − | |||
void loop(void) | void loop(void) | ||
{ | { | ||
Revision as of 07:44, 29 July 2022
Back to fejemis
Contents |
Drive Teensy
Block diagram with all interfaces and interface protocol
Front Teensy
Block diagram with all interfaces and interface protocol
GUI
Using USB
Using the bridge
Software structure
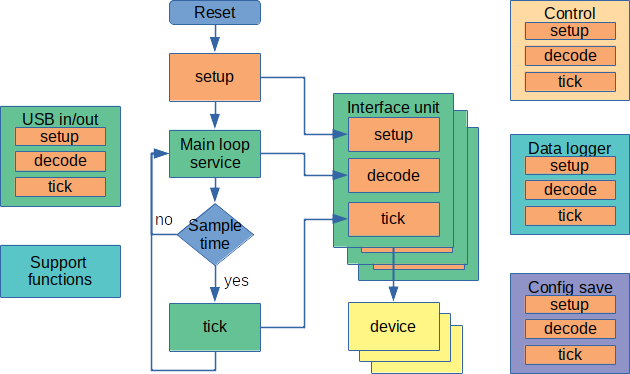
Figure: The Teensy software is structured with a main loop and a number of units. After reset all units are initialized in a setup function, after that the main loop is entered. The main loop services the USB and send commands to the units for decoding. At regular intervals, the sample clock tick, all units are called to execute any sample time function. Most units are interfaces to external devices such as IMU, motor drive or distance sensor. There is further support units for e.g. control.
Setup - loop overview
The setup and loop structure follows the Arduino sketch format. The file is a C++ file as the compilation is using a Makefile rather then the Arduino IDE.
The main file (main.cpp) code has this structure (shortened for clarity)
void setup() // INITIALIZATION
{
usb.setup();
led.setup();
imu.setup();
enc.setup();
sensor.setup();
motor.setup();
state.setup();
}
void loop(void)
{
usb.send("# Starting main loop\n");
while ( true )
{ // main loop
usb.tick(); // incoming command service
if ( startNewCycle ) // start of new control cycle
{
imu.tick(); // for heading estimate
sensor.tick(); // battery maintenance
irdist.tick(); // distance sensor
enc.tick(); // wheel encoder and odometry
state.tick(); // diagnostics and emergency stop
control.tick(); // feedback control
motor.tick(); // motor control
}
}
}
Module structure
One file one interface.
Subscription
Standardized setup of data subscription
Command decode
On-line help.
Configuration save
Use of configuration flash.
Update tick
Sample rate and sensor calculation