Robobot architecture
(→RSE level 1) |
(→NASREM) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
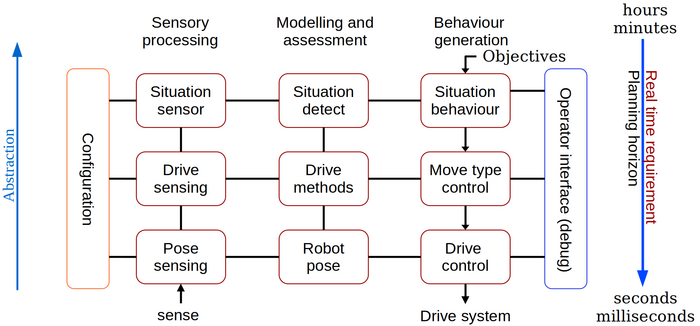
The software architecture is based on the old NASREM architecture, and this is the structure for the description on this page. | The software architecture is based on the old NASREM architecture, and this is the structure for the description on this page. | ||
| − | [[File:nasrem.png | | + | [[File:nasrem.png | 700px]] |
| + | |||
| + | Figure 1. The NASREM model divides the control software into a two-dimensional structure. The columns are software function: Sensor data processing, modelling and behaviour control. | ||
== RSE level 1 == | == RSE level 1 == | ||
Revision as of 12:12, 20 June 2023
Back to Robobot B
NASREM
The software architecture is based on the old NASREM architecture, and this is the structure for the description on this page.
Figure 1. The NASREM model divides the control software into a two-dimensional structure. The columns are software function: Sensor data processing, modelling and behaviour control.
RSE level 1
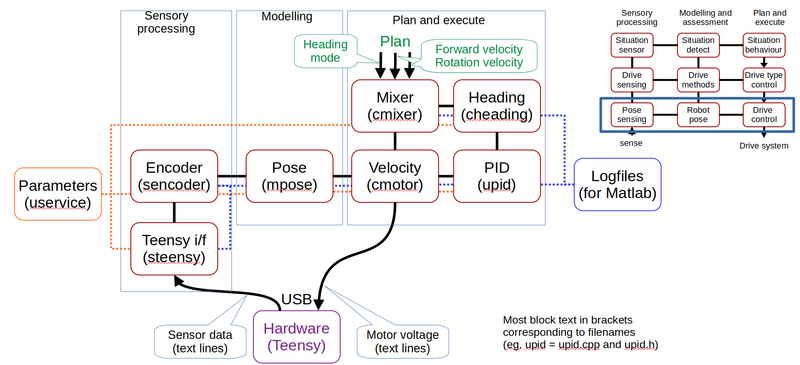
Figure 2. The lowest level in the control software. The encoder ticks are received form the hardware (from the Teensy microprocessor) in the sensor interface. The encoder values are then modeled into an odometry pose. The pose is used to control the wheel velocity using a PID controller. The desired wheel velocity for each wheel is generated in the mixer from a desired linear and rotational velocity.
RSE level 2
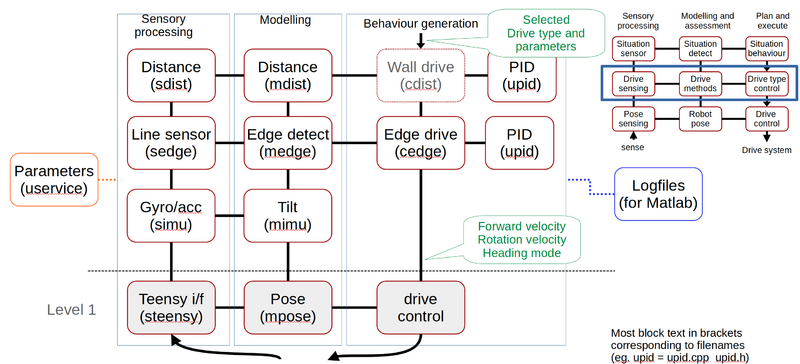
Figure 3. At level 2 further sensor data is received, modelled and used as optional control sources.