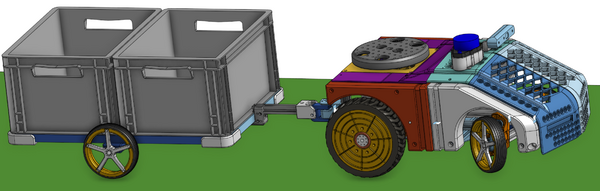
Scorpi
(→Raspberry pi) |
|||
| (27 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:scorpi_in_profile.png | + | [[File:scorpi_in_profile.png | 600px]] |
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Motor drive]] firmware | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Motor drive PCB]] with modifications | ||
==Development nodes== | ==Development nodes== | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Raspberry pi === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Raspberry pi 5 installation | ||
| + | |||
| + | * enable serial IO hardware (GPIO pin 14,15) - but it doesn't seem to work on pi-5, can't read or write. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Install packages: | ||
| + | libreadline-dev | ||
| + | libopencv-dev | ||
| + | libgpiod-dev | ||
| + | gpiod | ||
| + | cmake | ||
| + | subversion | ||
| + | aptitude | ||
| + | ntp | ||
| + | ntpdate | ||
| + | nmap | ||
| + | lsof | ||
| + | swig | ||
| + | dhcpcd | ||
| + | sudo apt install libreadline-dev libopencv-dev libgpiod-dev gpiod cmake subversion aptitude nmap lsof swig dhcp | ||
| + | |||
| + | === YDLidar (S4B) === | ||
| + | |||
| + | YDlidar serial connected like this: | ||
| + | |||
| + | YDLIDAR cable color Raspberry | ||
| + | 1 Vcc (5V) black 4 (5V) | ||
| + | 2 Tx red 10 (GPIO 15) (RxD) | ||
| + | 3 Rx white 8 (GPIO 14)(TxD) | ||
| + | 4 Gnd Yellow 6 (Ground) | ||
| + | 5 M_SCP Orange 18 (GPIO 24) | ||
| + | 6 Dev_enable Green 16 (GPIO 23) | ||
| + | 7 M_enable Blue 12 (GPIO 18) | ||
| + | 8 NC Purple 14 (ground, to use all pins) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Software YDLidar-SDK | ||
| + | |||
| + | From Git repository | ||
| + | |||
| + | $ mkdir -p git | ||
| + | $ cd git | ||
| + | $ git clone https://github.com/YDLIDAR/YDLidar-SDK.git | ||
| + | $ cd YDLidar-SDK | ||
| + | $ mkdir build | ||
| + | $ cd build | ||
| + | $ cmake .. | ||
| + | $ make -j4 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Ros2 Iron== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Installation on Raspberry Pi 5 running | ||
| + | default 64-bit OS: Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm) | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Base=== | ||
| + | Add en_DK.UTF-8 in this list | ||
| + | $ sudo dpkg-reconfigure locales | ||
| + | Then run | ||
| + | $ sudo update-locale LC_ALL=en_DK.UTF-8 LANG=en_DK.UTF-8 | ||
| + | $ export LANG=en_DK.UTF-8 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Compiled packages are not supported for Raspberry 64-bit OS, so install from source, | ||
| + | Followed: | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://docs.ros.org/en/iron/Installation/Alternatives/Ubuntu-Development-Setup.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | The result goes into ~/ros2_iron | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that ''rosdep'' fails in most cases, as the platform is not that much supported. | ||
| + | Manual dependency updates are therefore used in most cases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note, this command takes maybe 3 hours to compile all (on Raspberry Pi 5 - (8G memory): | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd ~/ros2_iron/ | ||
| + | colcon build --symlink-install | ||
| + | |||
| + | Add this line to ~/.bashrc | ||
| + | source /home/local/ros2_iron/install/setup.bash | ||
| + | |||
| + | The examples should now work (in separate terminals) | ||
| + | ros2 run demo_nodes_cpp talker | ||
| + | ros2 run demo_nodes_py listener | ||
| + | |||
| + | === ROS2 domain === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ros2 domain over local network | ||
| + | |||
| + | $export | grep ROS_ | ||
| + | |||
| + | could show | ||
| + | |||
| + | declare -x ROS_AUTOMATIC_DISCOVERY_RANGE="SUBNET" | ||
| + | declare -x ROS_DISTRO="iron" | ||
| + | declare -x ROS_DOMAIN_ID="8" | ||
| + | declare -x ROS_LOCALHOST_ONLY="0" | ||
| + | declare -x ROS_PYTHON_VERSION="3" | ||
| + | declare -x ROS_VERSION="2" | ||
| + | |||
| + | In this case, ROS cooperates with others on the local network who also have ROS_DOMAIN_ID="8." | ||
| + | |||
| + | If used, insert these into ~/.bashrc | ||
| + | export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=8 | ||
| + | export ROS_LOCALHOST_ONLY="0" | ||
| + | |||
| + | ROS_DOMAIN=0 is the default. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==YDLidar driver== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Make a new ROS2 workspace for this application, here called ''scorpi_ws'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | mkdir -p ~/scorpi/src | ||
| + | cd scorpi_ws/src | ||
| + | |||
| + | Get the modified YDLidar driver (modified for ''iron'') | ||
| + | |||
| + | ls | ||
| + | ydlidar_ros2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Modify scorpi_ws/src/ydlidar/params/ydlidar.yaml to the type of YDlidar you use, | ||
| + | For YDlidar X4 it could look like | ||
| + | ydlidar_node: | ||
| + | ros__parameters: | ||
| + | port: /dev/ttyUSB0 | ||
| + | frame_id: laser_frame | ||
| + | ignore_array: "" | ||
| + | baudrate: 128000 | ||
| + | samp_rate: 9 | ||
| + | resolution_fixed: true | ||
| + | singleChannel: false | ||
| + | auto_reconnect: true | ||
| + | reversion: true | ||
| + | isToFLidar: false | ||
| + | angle_max: 180.0 | ||
| + | angle_min: -180.0 | ||
| + | max_range: 16.0 | ||
| + | min_range: 0.1 | ||
| + | frequency: 10.0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now build the driver | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd .. | ||
| + | colcon build | ||
| + | |||
| + | You should get a few warnings only. | ||
| + | |||
| + | With the YDLidar X4 connected test with the driver nodes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd ~/scorpi_ws | ||
| + | ros2 run ydlidar ydlidar_node | ||
| + | |||
| + | And get something like: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [YDLIDAR INFO] Current ROS Driver Version: 1.4.5 | ||
| + | [YDLIDAR INFO] port: /dev/ttyUSB0 | ||
| + | [YDLIDAR INFO] baudrate: 128000 | ||
| + | [YDLIDAR]:SDK Version: 1.4.5 | ||
| + | [YDLIDAR]:Lidar running correctly ! The health status: good | ||
| + | [YDLIDAR] Connection established in [/dev/ttyUSB0][128000]: | ||
| + | Firmware version: 1.4 | ||
| + | Hardware version: 1 | ||
| + | Model: X4 | ||
| + | Serial: 2018060400000037 | ||
| + | [YDLIDAR INFO] Current Sampling Rate : 5K | ||
| + | [YDLIDAR INFO] Now YDLIDAR is scanning ...... | ||
| + | |||
| + | The node should publish /scan, e.g.: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ros2 topic list | ||
| + | /parameter_events | ||
| + | /rosout | ||
| + | /scan | ||
| + | |||
| + | == SLAM toolbox == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fetch the SLAM toolbox from https://github.com/SteveMacenski/slam_toolbox.git | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd ~/scorpi_ws/src | ||
| + | git clone https://github.com/SteveMacenski/slam_toolbox.git | ||
| + | |||
| + | This can not be build right away, as some dependencies are missing | ||
| + | |||
| + | sudo apt install libsuitesparse-dev | ||
| + | sudo apt install libeigen3-dev | ||
| + | sudo apt install libceres-dev | ||
| + | sudo apt install libbondcpp-dev | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd ~/scorpi_ws | ||
| + | colcon build | ||
| + | |||
| + | Compile failed with: | ||
| + | |||
| + | In file included from /home/local/scorpi_ws/src/slam_toolbox/src/slam_toolbox_common.cpp:23: | ||
| + | /home/local/scorpi_ws/src/slam_toolbox/include/slam_toolbox/slam_toolbox_common.hpp:34:10: fatal error: bondcpp/bond.hpp: | ||
| + | No such file or directory | ||
| + | 34 | #include "bondcpp/bond.hpp" | ||
| + | |||
| + | It seems like bond.hpp is not included in the version of libbondcpp-dev. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bond is used by the lifecycle manager - that can be disabled. So, assuming it will run without, I removed all references to bond in | ||
| + | include/slam_toolbox/slam_toolbox_common.hpp | ||
| + | src/slam_toolbox_common.cpp | ||
| + | Two include files, one pointer in the hpp file, two functions and two calls to these functions in the cpp file. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then the package compiled OK. | ||
Latest revision as of 18:39, 28 April 2024
Contents |
[edit] Overview
Motor drive firmware
Motor drive PCB with modifications
[edit] Development nodes
[edit] Raspberry pi
Raspberry pi 5 installation
- enable serial IO hardware (GPIO pin 14,15) - but it doesn't seem to work on pi-5, can't read or write.
Install packages:
libreadline-dev libopencv-dev libgpiod-dev gpiod cmake subversion aptitude ntp ntpdate nmap lsof swig dhcpcd sudo apt install libreadline-dev libopencv-dev libgpiod-dev gpiod cmake subversion aptitude nmap lsof swig dhcp
[edit] YDLidar (S4B)
YDlidar serial connected like this:
YDLIDAR cable color Raspberry 1 Vcc (5V) black 4 (5V) 2 Tx red 10 (GPIO 15) (RxD) 3 Rx white 8 (GPIO 14)(TxD) 4 Gnd Yellow 6 (Ground) 5 M_SCP Orange 18 (GPIO 24) 6 Dev_enable Green 16 (GPIO 23) 7 M_enable Blue 12 (GPIO 18) 8 NC Purple 14 (ground, to use all pins)
Software YDLidar-SDK
From Git repository
$ mkdir -p git $ cd git $ git clone https://github.com/YDLIDAR/YDLidar-SDK.git $ cd YDLidar-SDK $ mkdir build $ cd build $ cmake .. $ make -j4
[edit] Ros2 Iron
Installation on Raspberry Pi 5 running default 64-bit OS: Debian GNU/Linux 12 (bookworm)
[edit] Base
Add en_DK.UTF-8 in this list
$ sudo dpkg-reconfigure locales
Then run
$ sudo update-locale LC_ALL=en_DK.UTF-8 LANG=en_DK.UTF-8 $ export LANG=en_DK.UTF-8
Compiled packages are not supported for Raspberry 64-bit OS, so install from source, Followed:
https://docs.ros.org/en/iron/Installation/Alternatives/Ubuntu-Development-Setup.html
The result goes into ~/ros2_iron
Note that rosdep fails in most cases, as the platform is not that much supported. Manual dependency updates are therefore used in most cases.
Note, this command takes maybe 3 hours to compile all (on Raspberry Pi 5 - (8G memory):
cd ~/ros2_iron/ colcon build --symlink-install
Add this line to ~/.bashrc
source /home/local/ros2_iron/install/setup.bash
The examples should now work (in separate terminals)
ros2 run demo_nodes_cpp talker ros2 run demo_nodes_py listener
[edit] ROS2 domain
Ros2 domain over local network
$export | grep ROS_
could show
declare -x ROS_AUTOMATIC_DISCOVERY_RANGE="SUBNET" declare -x ROS_DISTRO="iron" declare -x ROS_DOMAIN_ID="8" declare -x ROS_LOCALHOST_ONLY="0" declare -x ROS_PYTHON_VERSION="3" declare -x ROS_VERSION="2"
In this case, ROS cooperates with others on the local network who also have ROS_DOMAIN_ID="8."
If used, insert these into ~/.bashrc
export ROS_DOMAIN_ID=8 export ROS_LOCALHOST_ONLY="0"
ROS_DOMAIN=0 is the default.
[edit] YDLidar driver
Make a new ROS2 workspace for this application, here called scorpi_ws
mkdir -p ~/scorpi/src cd scorpi_ws/src
Get the modified YDLidar driver (modified for iron)
ls ydlidar_ros2
Modify scorpi_ws/src/ydlidar/params/ydlidar.yaml to the type of YDlidar you use, For YDlidar X4 it could look like
ydlidar_node: ros__parameters: port: /dev/ttyUSB0 frame_id: laser_frame ignore_array: "" baudrate: 128000 samp_rate: 9 resolution_fixed: true singleChannel: false auto_reconnect: true reversion: true isToFLidar: false angle_max: 180.0 angle_min: -180.0 max_range: 16.0 min_range: 0.1 frequency: 10.0
Now build the driver
cd .. colcon build
You should get a few warnings only.
With the YDLidar X4 connected test with the driver nodes.
cd ~/scorpi_ws ros2 run ydlidar ydlidar_node
And get something like:
[YDLIDAR INFO] Current ROS Driver Version: 1.4.5 [YDLIDAR INFO] port: /dev/ttyUSB0 [YDLIDAR INFO] baudrate: 128000 [YDLIDAR]:SDK Version: 1.4.5 [YDLIDAR]:Lidar running correctly ! The health status: good [YDLIDAR] Connection established in [/dev/ttyUSB0][128000]: Firmware version: 1.4 Hardware version: 1 Model: X4 Serial: 2018060400000037 [YDLIDAR INFO] Current Sampling Rate : 5K [YDLIDAR INFO] Now YDLIDAR is scanning ......
The node should publish /scan, e.g.:
ros2 topic list /parameter_events /rosout /scan
[edit] SLAM toolbox
Fetch the SLAM toolbox from https://github.com/SteveMacenski/slam_toolbox.git
cd ~/scorpi_ws/src git clone https://github.com/SteveMacenski/slam_toolbox.git
This can not be build right away, as some dependencies are missing
sudo apt install libsuitesparse-dev sudo apt install libeigen3-dev sudo apt install libceres-dev sudo apt install libbondcpp-dev
cd ~/scorpi_ws colcon build
Compile failed with:
In file included from /home/local/scorpi_ws/src/slam_toolbox/src/slam_toolbox_common.cpp:23: /home/local/scorpi_ws/src/slam_toolbox/include/slam_toolbox/slam_toolbox_common.hpp:34:10: fatal error: bondcpp/bond.hpp: No such file or directory 34 | #include "bondcpp/bond.hpp"
It seems like bond.hpp is not included in the version of libbondcpp-dev.
Bond is used by the lifecycle manager - that can be disabled. So, assuming it will run without, I removed all references to bond in
include/slam_toolbox/slam_toolbox_common.hpp src/slam_toolbox_common.cpp
Two include files, one pointer in the hpp file, two functions and two calls to these functions in the cpp file.
Then the package compiled OK.