Robobot mission
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
The [[mission code]] is described in a bit more detail here. | The [[mission code]] is described in a bit more detail here. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Installation== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Get software=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Get the ROBOBOT software from the svn repository: | ||
| + | |||
| + | svn checkout svn://repos.gbar.dtu.dk/jcan/regbot/mission mission | ||
| + | |||
| + | or just update if there already | ||
| + | |||
| + | svn up | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Compile=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | To be able to compile the demo software CMAKE needs also to use the user installed library (raspicam installed above), | ||
| + | so add the following line to ~/.bashrc: | ||
| + | |||
| + | export CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH=/usr/local/lib | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then build Makefiles and compile: | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd ~/mission | ||
| + | mkdir -p build | ||
| + | cd build | ||
| + | cmake .. | ||
| + | make -j3 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then test-run the application: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ./mission | ||
| + | |||
| + | It should print that the camera is open and the bridge is connected to the REGBOT hardware. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Sound== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The robot has small speakers | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Music=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Speak=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | system("espeak \"bettina reached point 3\" -ven+f4 -a30 -s130"); | ||
| + | |||
| + | This line makes the robot say "bettina reached point 3" the parameters "-a30" turns amplitude down to 30%, "-ven+f4" sets language to english with female voice 4 and "-s130" makes the speech a little slower and easier to understand. | ||
| + | It requires that espeak is installed (sudo apt install espeak). | ||
| + | |||
| + | To use on Raspberry pi, it is better to use | ||
| + | |||
| + | system("espeak \"Mission paused.\" -ven+f4 -s130 -a60 2>/dev/null &"); | ||
| + | |||
| + | The "2>/dev/null" tell that error messages should be dumped, and the final "&" say that it should run in the background (not to pause the mission). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===AruCo Marker=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The camera class contains some functions to detect Aruco markers. | ||
| + | It it described in more details on [[AruCo Markers]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Software documentation (doxygen)=== | ||
| + | |||
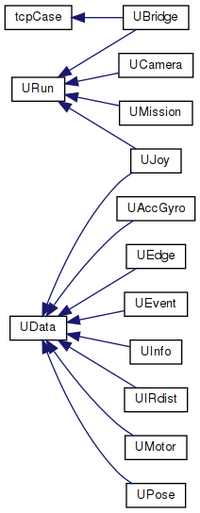
| + | [[File:inherit_graph_2.png | 200px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Figure: generated with doxygen http://aut.elektro.dtu.dk/robobot/doc/html/classes.html | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The classes that inherit from UData are classes that makes data available for the mission, e.g. joystick buttons (in UJoy) event flags (in UEvent) or IR distance data (in UIRdist). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The classes that inherit from URun has a thread running to receive data from an external source, e.g. UBridge that handles communication with the ROBOBOT_BRIDGE. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The camera class (UCamera) is intended to do the image processing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====HTML documentation - Doxygen==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | To generate doxygen html files go to mission directory and run doxygen. | ||
| + | |||
| + | cd ~/mission | ||
| + | doxygen Doxyfile | ||
| + | |||
| + | then open the index.html with a browser. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If doxygen is not installed, then install using | ||
| + | |||
| + | sudo apt install doxygen | ||
Revision as of 12:04, 1 January 2020
Back to robobot
Contents |
Robobot mission software
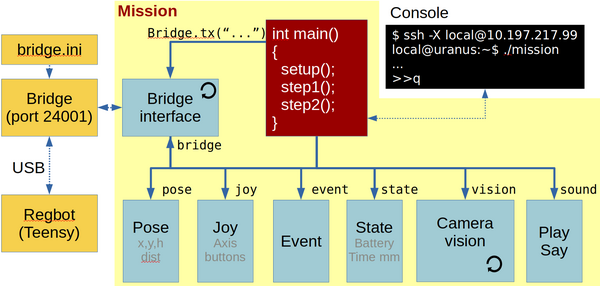
This figure shows the mission functional blocks. The main connection is to the robobot_bridge, through which the robot is controlled. The red mission block is the main block, where the behaviour is controlled. To help decide and control the behaviour, there is a number of data elements available in the bottom row of boxes, available through the bridge. A camera block is available, where image processing is assumed to happen. From the camera block, there is support for ArUco marker detection.
The blocks marked with a circle arrow is running their own thread. The yellow boxes are features available outside the mission application.
Main
The main block is the entry point of the application. This block creates all the other blocks, and if there is a successful connection to the robobot_bridge, then the mission thread is started, and the main thread now just listens for keyboard input.
The keyboard input (console input) can be used to get status of the individual blocks and issue some simple (mostly debugging) commands.
Press h (and enter) to get a list of features:
>> h # got 'h' n=1 # mission command options # h This help # a Do an ArUco analysis of a frame (no debug - faster) # d Do an ArUco analysis of a frame (with debug images) # c Capture an image and save to disk (image*.png) # o Loop-test for steady ArUco marker (makes logfile) # t 99 Camera tilt degrees (positive down), is 10.0 deg # p 99 Camera pan (Yaw) degrees (positive CCV) is 0.0 deg # lo xxx Open log for xxx (pose 0, hbt 0, bridge 0, imu 0 # ir 0, motor 0, joy 0, event 0, cam 0, aruco 1) # lc xxx Close log for xxx # s Status (all) # q Quit now
Logfiles
The data blocks have a data logger feature that can be enabled and disabled. The interface logfile will be in a text format for MATLAB import. The name of the logfile will include date and time, and will therefore not overwrite the previous logfile.
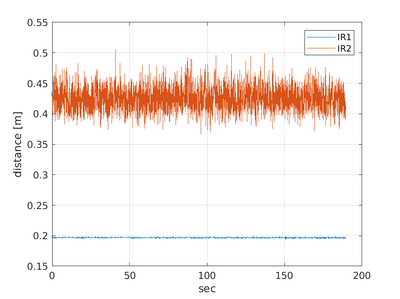
The IR logfile could be named 'log_irdist_20191227_095545.054.txt' look like this:
% robobot mission IR distance log % 1 Timestamp in seconds % 2 IR 1 distance [meter] % 3 IR 2 distance [meter] % 4 IR 1 raw [AD value] % 5 IR 2 raw [AD value] 1577436945.093 0.197 0.436 44943 15573 1577436945.139 0.197 0.421 44925 16430 1577436945.180 0.197 0.416 44896 16768 1577436945.225 0.196 0.410 44996 17123 1577436945.266 0.197 0.404 44922 17463 1577436945.311 0.197 0.423 44920 16341
And can be displayed in MATLAB using a script like this
data = load('log_irdist_20191227_095545.054.txt');
h = figure(200)
hold off
plot(data(:,1) - data(1,1), data(:,2))
hold on
plot(data(:,1) - data(1,1), data(:,3))
grid on
legend('IR1', 'IR2')
xlabel('sec')
ylabel('distance [m]')
saveas(h, 'ir_plot.png')
And in this case, the plot shows:
The plot shows that longer distances (IR2) have more noise than short distances (IR1).
Bridge
This part handles the interface with the regbot_bridge application. This two-way communication handles each direction individually.
Sending messages is mostly handled by the mission block, here regular updates of data is requested for the data blocks - e.g. robot pose, joystick buttons, IR-sensor measurements etc.
The receiving part of the bridge is always waiting for messages and distribute them for the relevant data block for decoding.
In a normal setup, about 150 messages will be received each second.
Data elements
This is a list of the features of each of the data elements.
IMU
Has
IR-dist
Has
Pose
Joy
Motor
Info
The info block holds som static data, but also data from the heartbeat message - the only part that can be logged).
Event
Holds all 32 events. The logfile has a list of when each of then has been set or cleared.
Edge
The edge sensor (also called line sensor).
Camera
The camera interface sets the camera to 1280 x 960 pixels at 30 frames per second.
...
ArUco
This part of the camera system is configured to detect ArUco codes with their position relative to the robot. The position is in (x, y, z), where x is forward, y is left and z is up. The reference position is the center between the driving wheels at ground level.
Mission
The mission block has access to all the other elements and controls the performance of the robot.
The mission code is described in a bit more detail here.
Installation
Get software
Get the ROBOBOT software from the svn repository:
svn checkout svn://repos.gbar.dtu.dk/jcan/regbot/mission mission
or just update if there already
svn up
Compile
To be able to compile the demo software CMAKE needs also to use the user installed library (raspicam installed above), so add the following line to ~/.bashrc:
export CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH=/usr/local/lib
Then build Makefiles and compile:
cd ~/mission mkdir -p build cd build cmake .. make -j3
Then test-run the application:
./mission
It should print that the camera is open and the bridge is connected to the REGBOT hardware.
Sound
The robot has small speakers
Music
Speak
system("espeak \"bettina reached point 3\" -ven+f4 -a30 -s130");
This line makes the robot say "bettina reached point 3" the parameters "-a30" turns amplitude down to 30%, "-ven+f4" sets language to english with female voice 4 and "-s130" makes the speech a little slower and easier to understand. It requires that espeak is installed (sudo apt install espeak).
To use on Raspberry pi, it is better to use
system("espeak \"Mission paused.\" -ven+f4 -s130 -a60 2>/dev/null &");
The "2>/dev/null" tell that error messages should be dumped, and the final "&" say that it should run in the background (not to pause the mission).
AruCo Marker
The camera class contains some functions to detect Aruco markers. It it described in more details on AruCo Markers.
Software documentation (doxygen)
Figure: generated with doxygen http://aut.elektro.dtu.dk/robobot/doc/html/classes.html
The classes that inherit from UData are classes that makes data available for the mission, e.g. joystick buttons (in UJoy) event flags (in UEvent) or IR distance data (in UIRdist).
The classes that inherit from URun has a thread running to receive data from an external source, e.g. UBridge that handles communication with the ROBOBOT_BRIDGE.
The camera class (UCamera) is intended to do the image processing.
HTML documentation - Doxygen
To generate doxygen html files go to mission directory and run doxygen.
cd ~/mission doxygen Doxyfile
then open the index.html with a browser.
If doxygen is not installed, then install using
sudo apt install doxygen